# diffbot
**Repository Path**: TUAL/diffbot
## Basic Information
- **Project Name**: diffbot
- **Description**: No description available
- **Primary Language**: Unknown
- **License**: BSD-3-Clause
- **Default Branch**: noetic-devel
- **Homepage**: None
- **GVP Project**: No
## Statistics
- **Stars**: 0
- **Forks**: 0
- **Created**: 2024-11-28
- **Last Updated**: 2025-03-07
## Categories & Tags
**Categories**: Uncategorized
**Tags**: None
## README
# DiffBot

[](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/ros-mobile-robots.github.io/actions/workflows/ci.yml)
DiffBot是一个自主差速驱动机器人,有两个轮子。它的主要处理单元是运行Ubuntu Mate 20.04和ROS 1(ROS Noetic)中间件的树莓派4 B。该仓库包含ROS驱动程序包、用于实际机器人的ROS Control硬件接口以及用于模拟DiffBot的配置。格式化文档可以在以下网址找到:https://ros-mobile-robots.com。
| DiffBot | Lidar SLAMTEC RPLidar A2 |
|:-------:|:-----------------:|
| [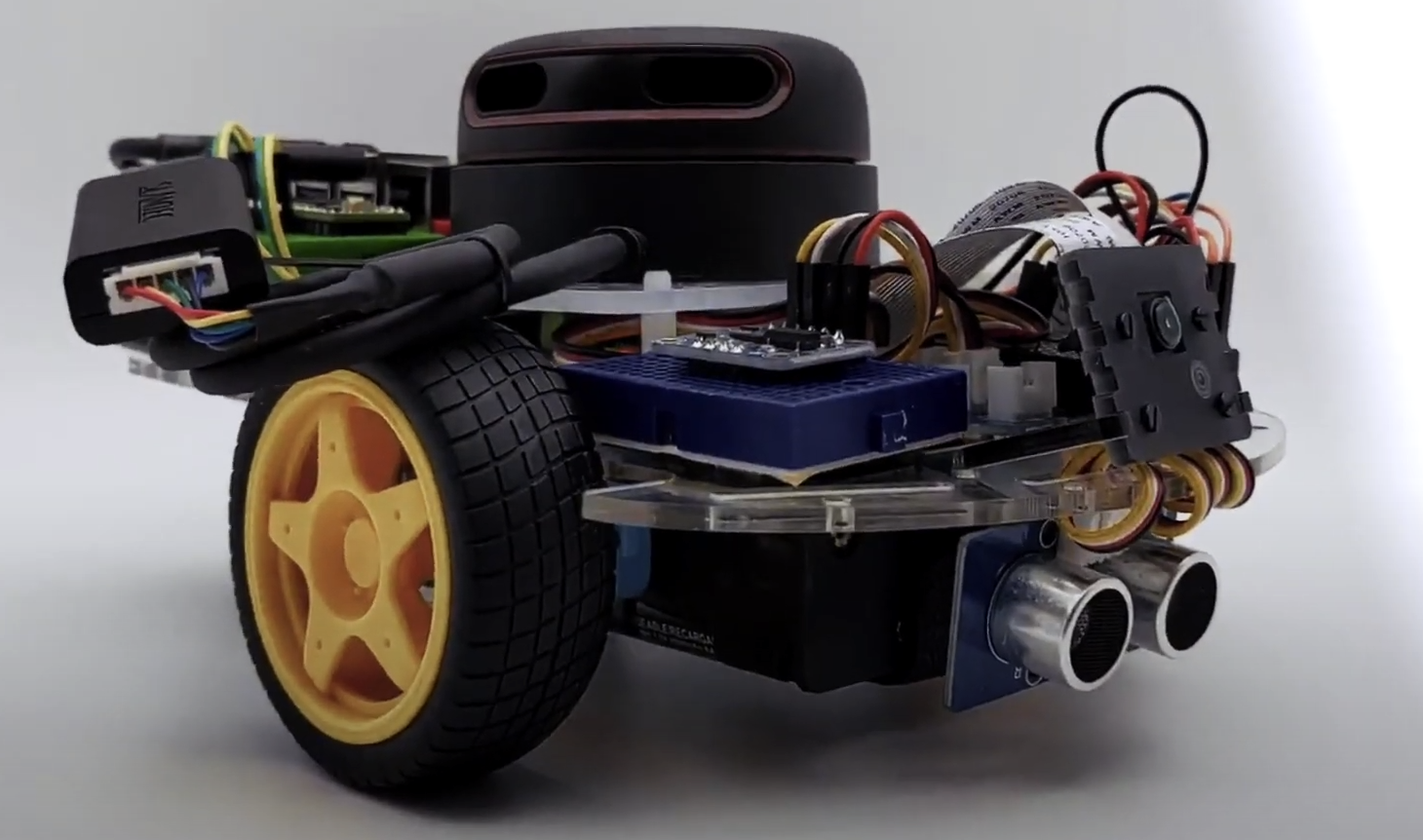 ](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik) | [
](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik) | [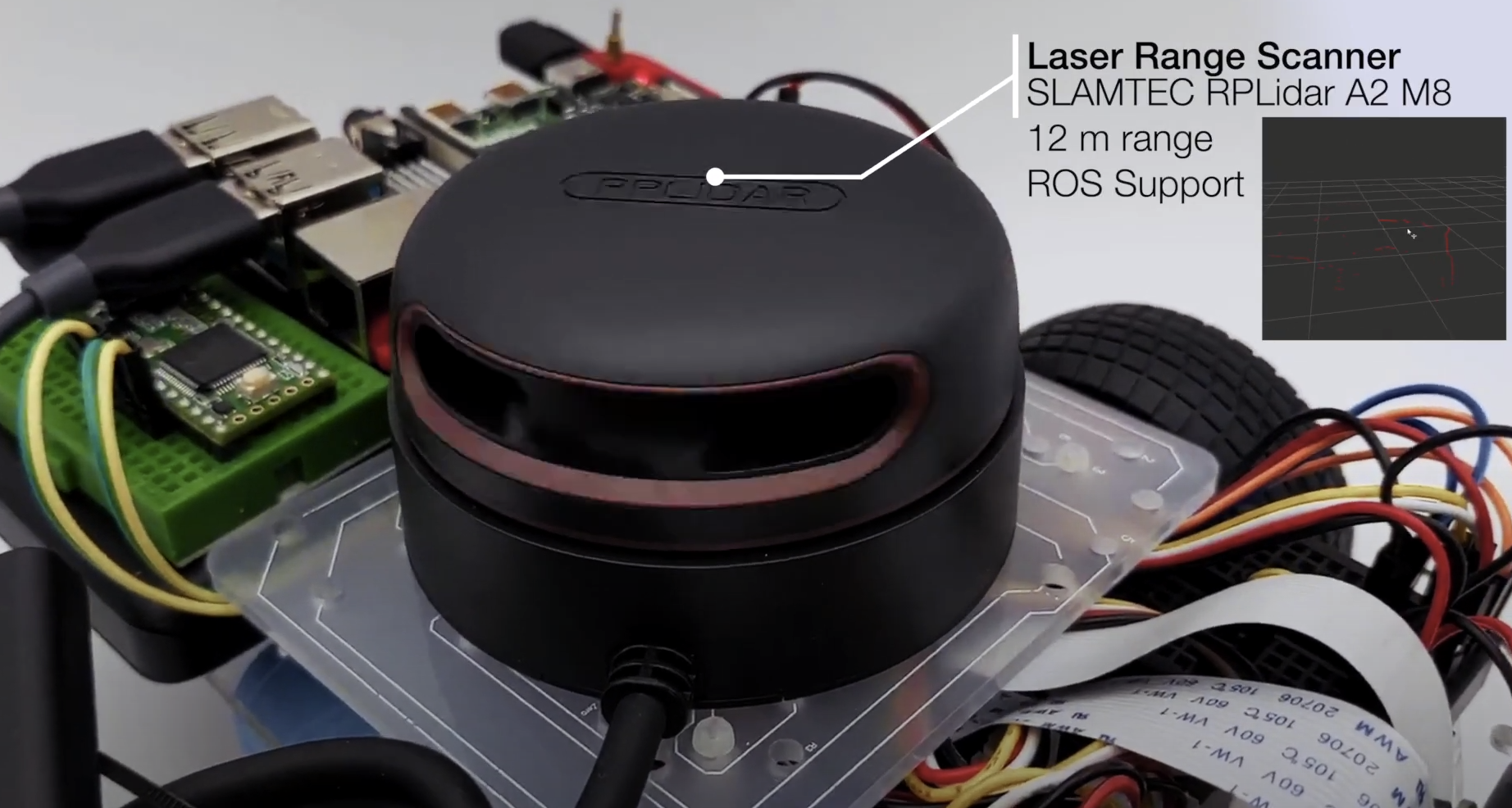 ](https://fjp.at/projects/diffbot/) |
如果您正在寻找可3D打印的模块化底盘,请参见[`remo_description`](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/remo_description)仓库。您可以直接将其与此`diffbot`仓库的软件一起使用。
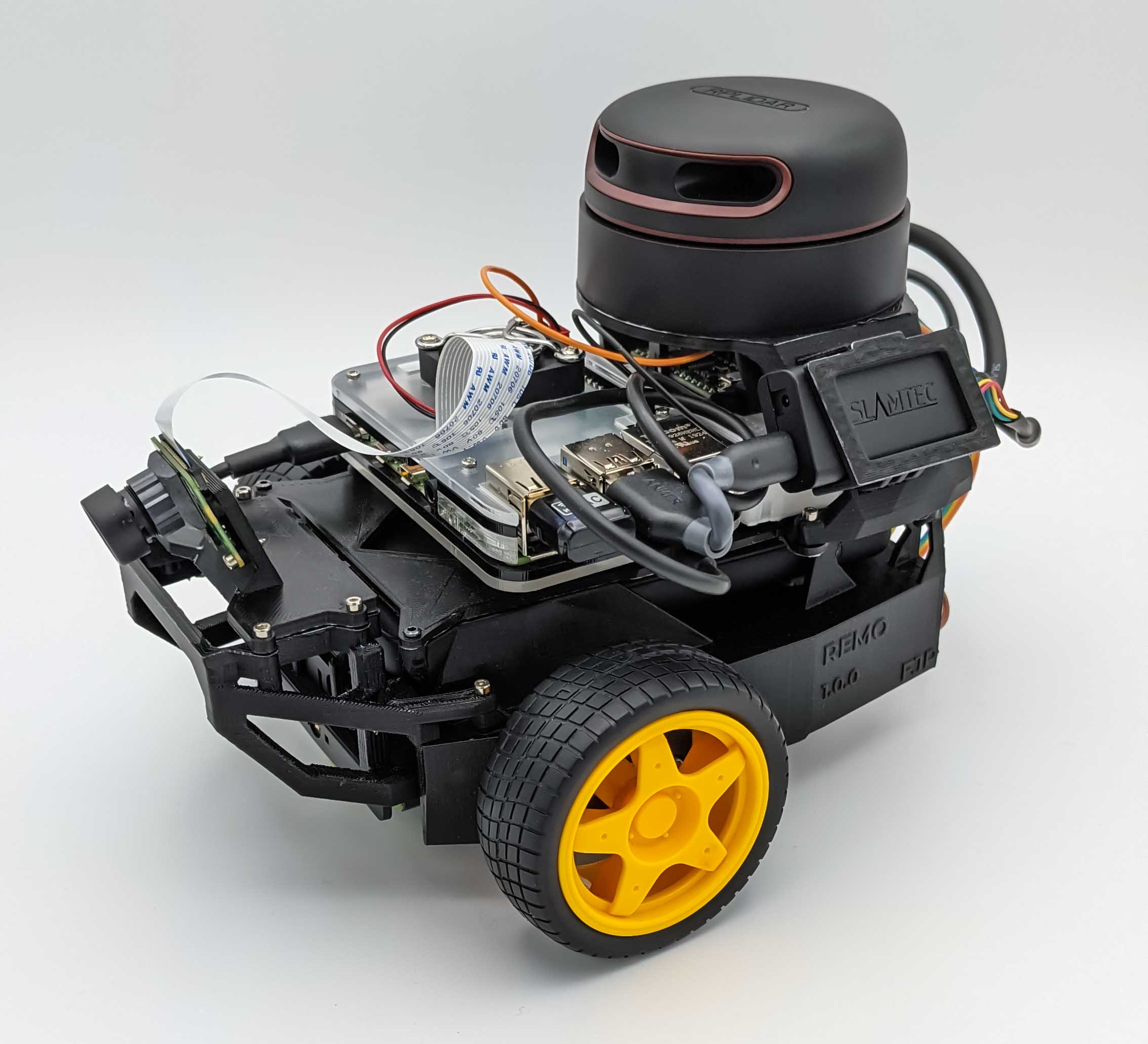
| Remo | Gazebo仿真 | RViz |
|:-------:|:-----------------:|:----:|
| [
](https://fjp.at/projects/diffbot/) |
如果您正在寻找可3D打印的模块化底盘,请参见[`remo_description`](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/remo_description)仓库。您可以直接将其与此`diffbot`仓库的软件一起使用。
| Remo | Gazebo仿真 | RViz |
|:-------:|:-----------------:|:----:|
| [ ](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik) | [
](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik) | [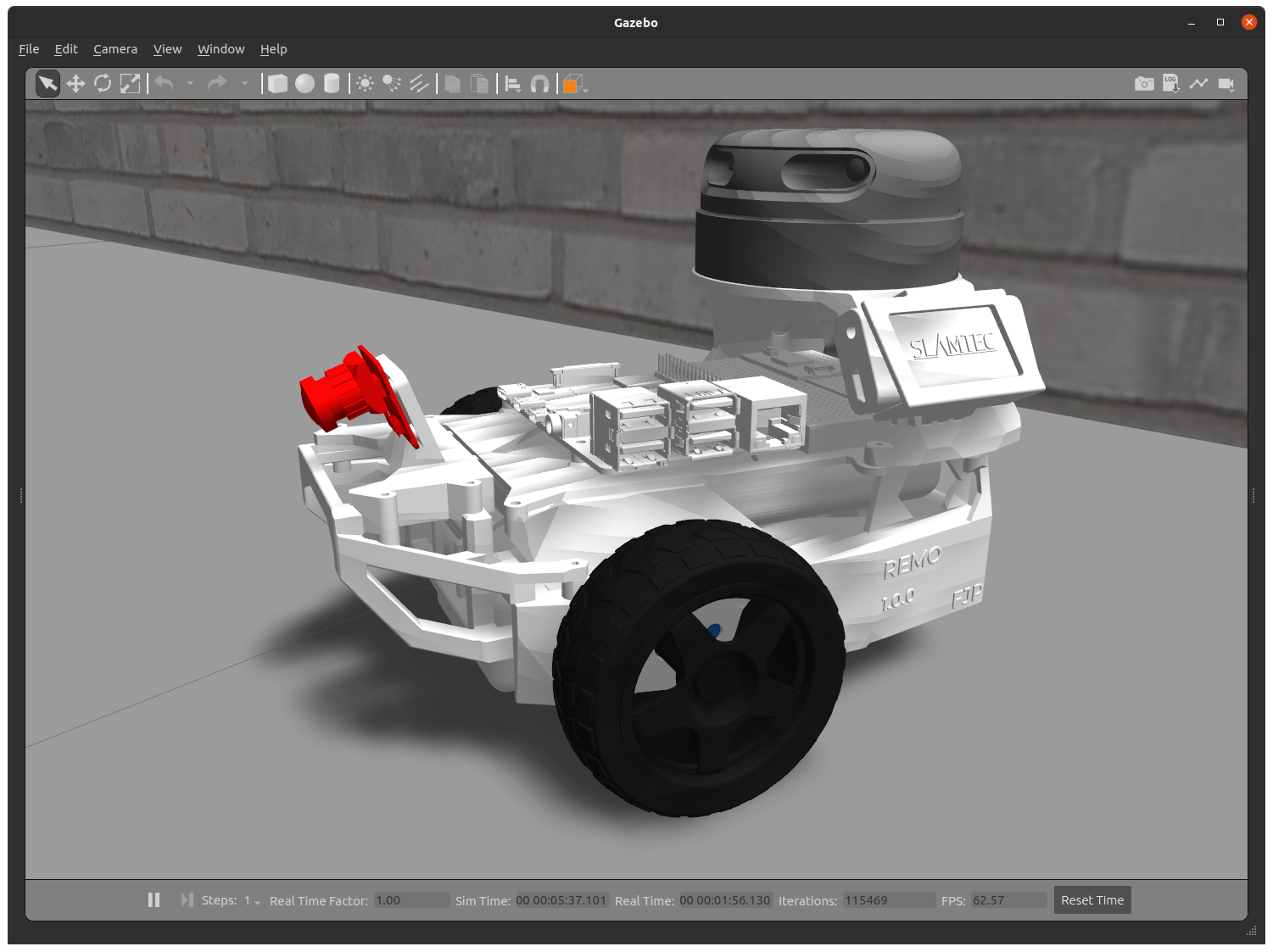 ](https://github.com/fjp/diffbot) | [
](https://github.com/fjp/diffbot) | [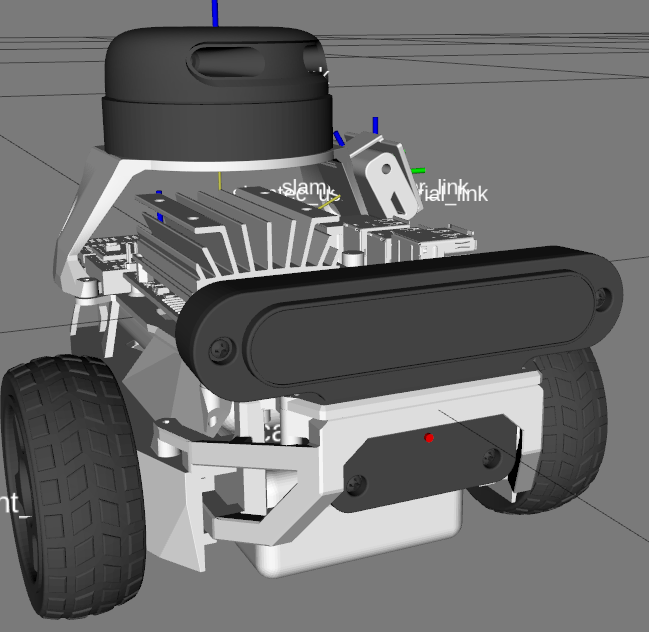 ](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/diffbot) |
它为不同的相机模块提供安装支架,如Raspi Cam v2、OAK-1、OAK-D,您甚至可以根据需要设计自己的支架。通过两个可更换的层板,它还支持不同的单板计算机(树莓派和Nvidia Jetson Nano)。您同样可以自由创建自己的层板。
## 演示
### SLAM和导航
| 实际机器人 | Gazebo仿真 |
|:-------:|:-----------------:|
| [
](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/diffbot) |
它为不同的相机模块提供安装支架,如Raspi Cam v2、OAK-1、OAK-D,您甚至可以根据需要设计自己的支架。通过两个可更换的层板,它还支持不同的单板计算机(树莓派和Nvidia Jetson Nano)。您同样可以自由创建自己的层板。
## 演示
### SLAM和导航
| 实际机器人 | Gazebo仿真 |
|:-------:|:-----------------:|
| [ ](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik) | [
](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik) | [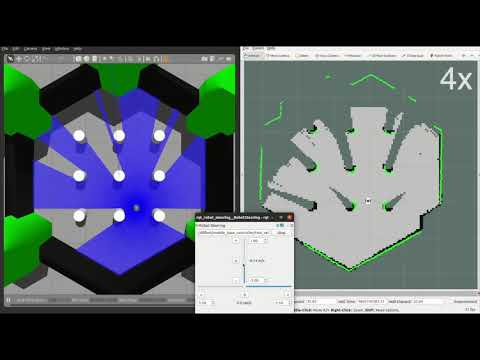 ](https://youtu.be/gLlo5V-BZu0) [
](https://youtu.be/gLlo5V-BZu0) [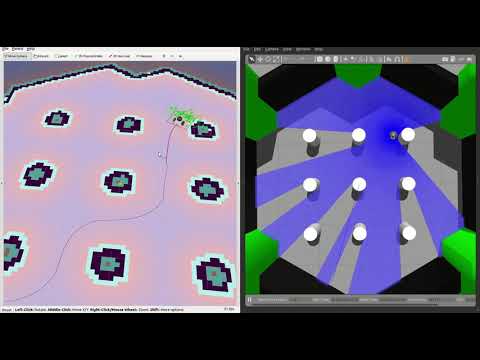 ](https://youtu.be/2SwFTrJ1Ofg) |
## :package: 软件包概述
- [`diffbot_base`](./diffbot_base): 包含[`controller_manager`](http://wiki.ros.org/controller_manager)控制循环的ROS Control硬件接口,用于实际机器人。该包的[`scripts`文件夹](./diffbot_base/scripts)包含运行在Teensy微控制器上的低级`base_controller`。
- [`diffbot_bringup`](./diffbot_bringup): 用于启动实际DiffBot机器人的硬件驱动程序(相机、激光雷达、IMU、超声波等)的启动文件。
- [`diffbot_control`](./diffbot_control): Gazebo仿真和实际机器人中使用的ROS Control [`diff_drive_controller`](http://wiki.ros.org/diff_drive_controller)的配置。
- [`diffbot_description`](./diffbot_description): DiffBot及其传感器的URDF描述。
- [`diffbot_gazebo`](./diffbot_gazebo): DiffBot的仿真专用启动和配置文件。
- [`diffbot_msgs`](./diffbot_msgs): DiffBot特定的消息定义,例如编码器数据的消息。
- [`diffbot_navigation`](./diffbot_navigation): 基于[`move_base`包](http://wiki.ros.org/move_base)的导航;启动和配置文件。
- [`diffbot_slam`](./diffbot_slam): 使用不同实现(例如[gmapping](http://wiki.ros.org/gmapping))的同时定位与地图构建,用于创建环境地图。
## 安装
这些软件包是为[ROS 1 Noetic](http://wiki.ros.org/noetic)在[Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa](https://releases.ubuntu.com/20.04/)上编写和测试的。
对于实际机器人,[Ubuntu Mate 20.04](https://ubuntu-mate.org/download/arm64/focal/) arm64版本安装在4GB的[树莓派4 B](https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-4-model-b/)上。移动机器人和工作PC之间的通信通过配置[ROS网络](http://wiki.ros.org/ROS/NetworkSetup)完成,详见[文档](./docs/ros-network-setup.md)。
### 依赖项
所需的Ubuntu软件包列在[文档](https://ros-mobile-robots.com/packages/packages-setup/#obtain-system-dependencies)的软件包部分。其他ROS catkin软件包如[`rplidar_ros`](https://github.com/Slamtec/rplidar_ros)需要克隆到catkin工作空间中。
为了实现自动化和简化的依赖项安装过程,请安装[`vcstool`](https://github.com/dirk-thomas/vcstool),它将在后续步骤中使用。
```console
sudo apt install python3-vcstool
```
### :hammer: 如何构建
要构建此仓库中的软件包(包括Remo机器人),请按照以下步骤操作:
1. `cd`进入现有的ROS Noetic [catkin工作空间](http://wiki.ros.org/catkin/Tutorials/create_a_workspace)或创建一个新的:
```console
mkdir -p catkin_ws/src
```
2. 在ROS Noetic catkin工作空间的`src`文件夹中克隆此仓库:
```console
cd catkin_ws/src
```
```console
git clone https://github.com/fjp/diffbot.git
```
3. 从catkin工作空间的根目录执行`vcs import`命令,并根据执行命令的位置(开发PC或Remo的SBC)导入`diffbot_dev.repos`或`remo_robot.repos` YAML文件,以克隆列出的依赖项。仅在开发机器上运行以下命令:
```
vcs import < src/diffbot/diffbot_dev.repos
```
在Remo机器人的SBC上运行以下命令:
```
vcs import < src/diffbot/remo_robot.repos
```
4. 使用以下[`rosdep`命令](http://wiki.ros.org/rosdep#Install_dependency_of_all_packages_in_the_workspace)安装catkin工作空间中所有软件包所需的二进制依赖项:
```
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
```
5. 安装所需依赖项后,构建catkin工作空间,可以使用[`catkin_make`](http://wiki.ros.org/catkin/commands/catkin_make):
```console
catkin_ws$ catkin_make
```
或使用[catkin-tools](https://catkin-tools.readthedocs.io/en/latest/):
```console
catkin_ws$ catkin build
```
6. 最后,根据使用的shell,使用`devel/setup.*`脚本source新构建的软件包:
对于bash使用:
```console
catkin_ws$ source devel/setup.bash
```
对于zsh使用:
```console
catkin_ws$ source devel/setup.zsh
```
## 使用方法
以下部分描述如何运行机器人仿真以及如何使用可用的软件包启动文件使用实际硬件。
### 使用ROS Control的Gazebo仿真
Control the robot inside Gazebo and view what it sees in RViz using the following launch file:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_control diffbot.launch
```
这将启动默认的diffbot世界`db_world.world`。
要运行[turtlebot3_world](https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/turtlebot3_simulations/tree/master/turtlebot3_gazebo/models/turtlebot3_world),
请确保将其下载到`~/.gazebo/models/`文件夹中,因为`turtlebot3_world.world`文件引用了`turtlebot3_world`模型。
下载完成后,您可以使用以下命令运行它:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_control diffbot.launch world_name:='$(find diffbot_gazebo)/worlds/turtlebot3_world.world'
```
| `db_world.world` | `turtlebot3_world.world` |
|:-------------------------------------:|:--------------------------------:|
|  | 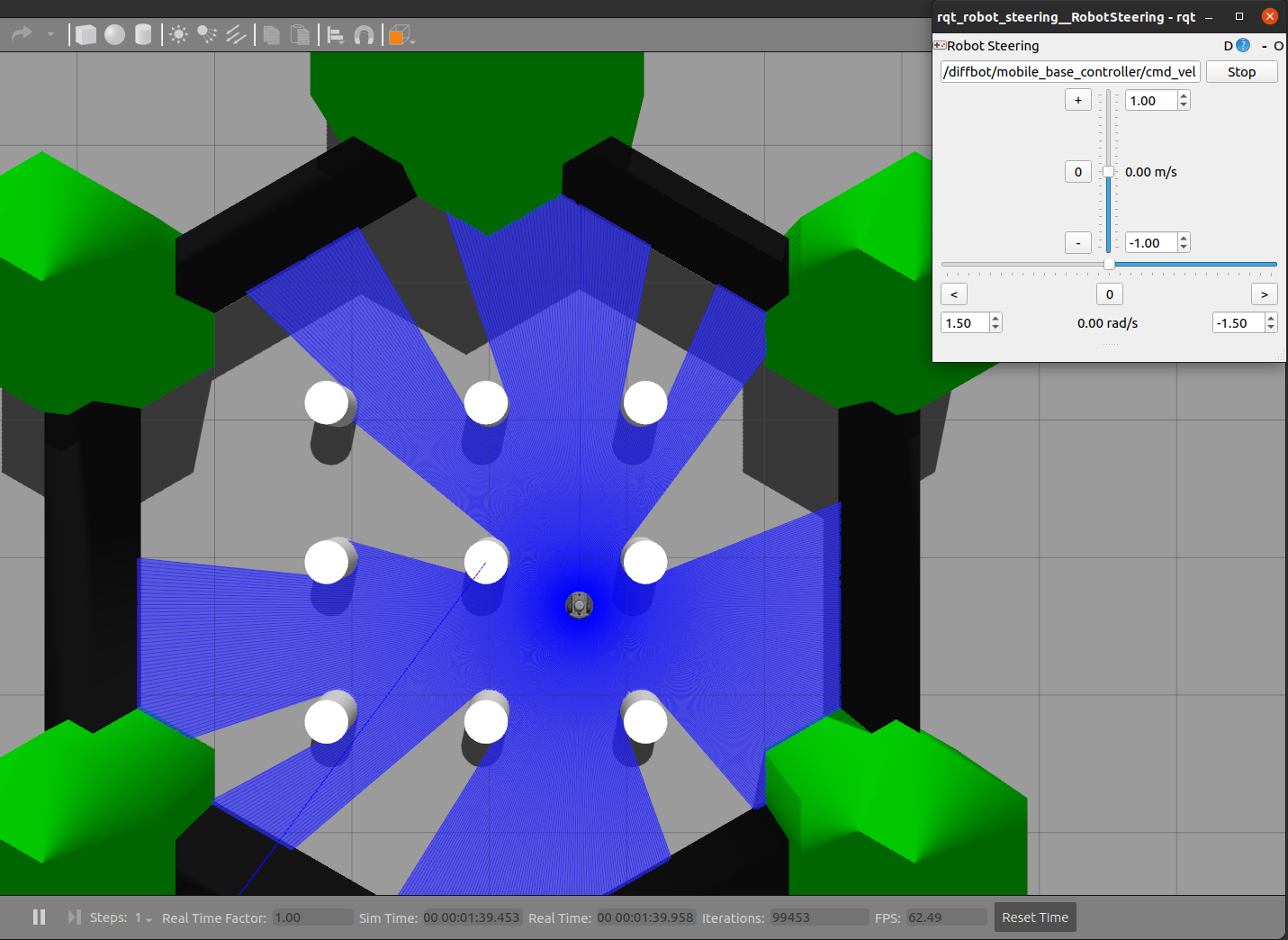 |
#### Navigation
要在Gazebo模拟器中的`db_world.world`环境中导航机器人,运行以下命令:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_navigation diffbot.launch
```
这使用了之前映射的`db_world.world`地图(位于[`diffbot_navigation/maps`](./diffbot_navigation/maps/)),该地图由[`map_server`](http://wiki.ros.org/map_server)提供服务。有了这个,你可以直接使用[RViz中的2D导航目标](http://wiki.ros.org/navigation/Tutorials/Using%20rviz%20with%20the%20Navigation%20Stack#A2D_Nav_Goal)让机器人在`db_world.world`中自主行驶。
[](https://youtu.be/2SwFTrJ1Ofg)
要运行`turtlebot3_world.world`(或您自己存储的世界和地图),请使用相同的`diffbot_navigation/launch/diffbot.launch`文件,但将`world_name`和`map_file`参数更改为您想要的世界和地图yaml文件:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_navigation diffbot.launch world_name:='$(find diffbot_gazebo)/worlds/turtlebot3_world.world' map_file:='$(find diffbot_navigation)/maps/map.yaml'
```
[](https://youtu.be/2SwFTrJ1Ofg)
#### SLAM
To map a new simulated environment using slam gmapping, first run
```console
roslaunch diffbot_gazebo diffbot.launch world_name:='$(find diffbot_gazebo)/worlds/turtlebot3_world.world'
```
and in a second terminal execute
```console
roslaunch diffbot_slam diffbot_slam.launch slam_method:=gmapping
```
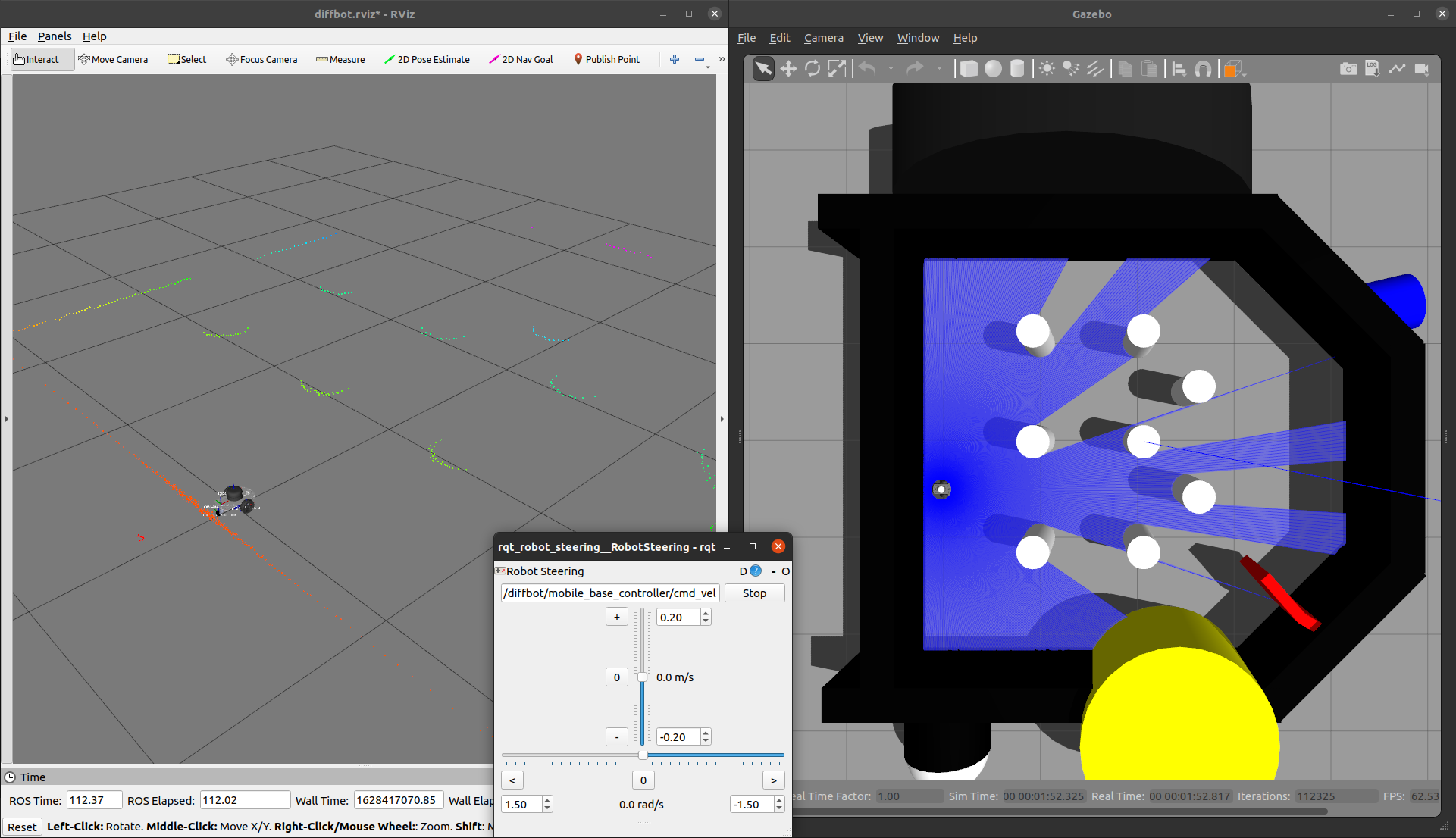
Then explore the world with the [`teleop_twist_keyboard`](http://wiki.ros.org/teleop_twist_keyboard) or with the already launched [`rqt_robot_steering`](https://wiki.ros.org/rqt_robot_steering) GUI plugin:
[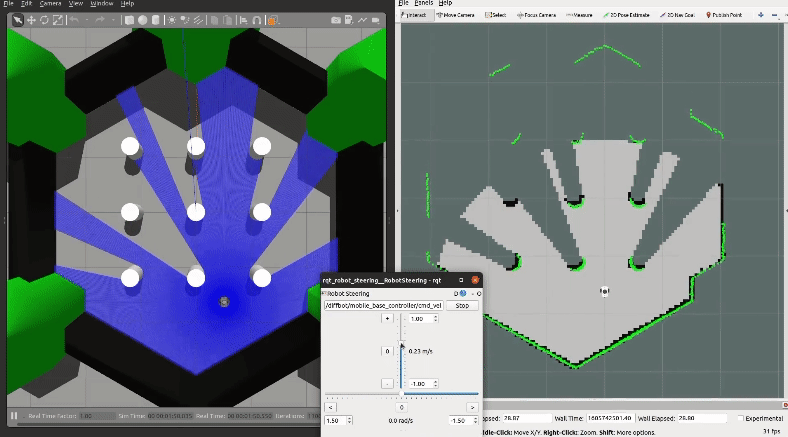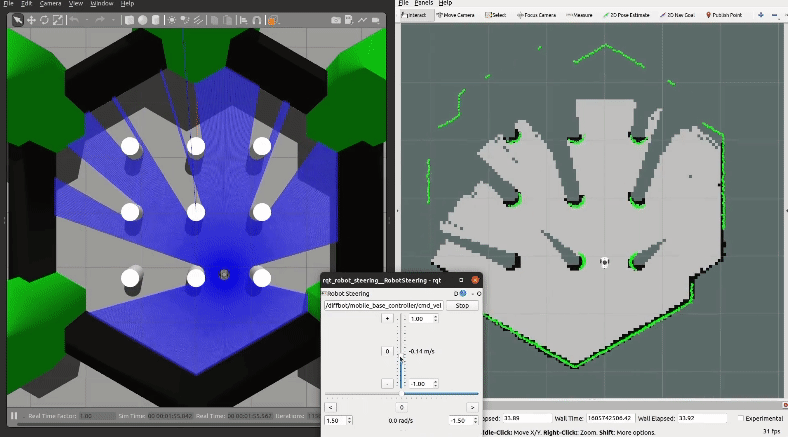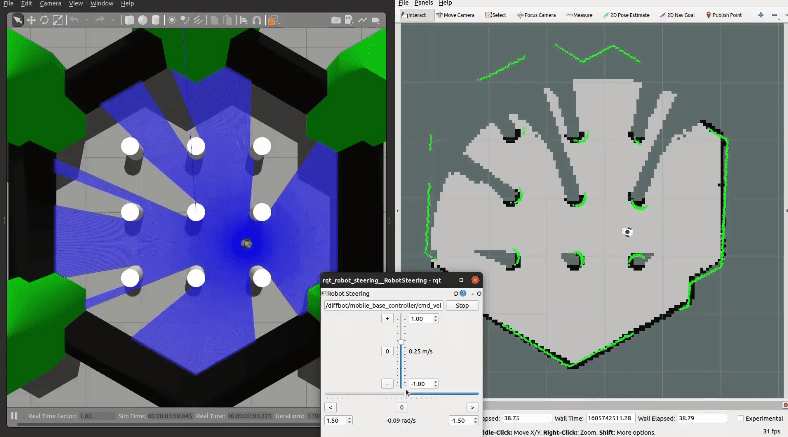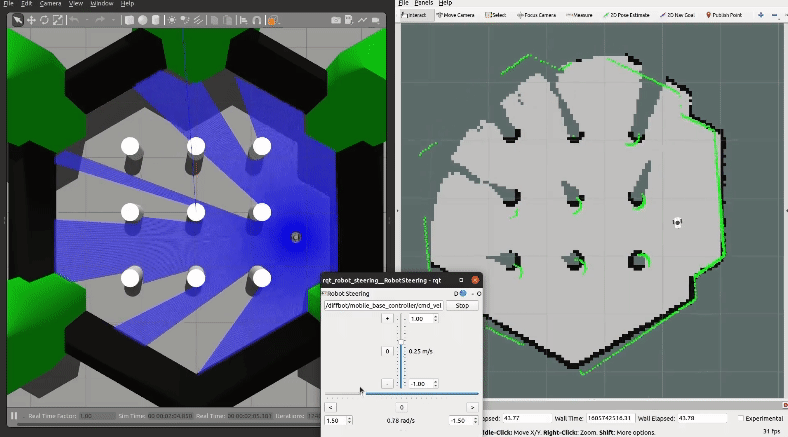](https://youtu.be/gLlo5V-BZu0)
When you finished exploring the new world, use the [`map_saver`](http://wiki.ros.org/map_server#map_saver) node from the [`map_server`](http://wiki.ros.org/map_server) package to store the mapped enviornment:
```console
rosrun map_server map_saver -f ~/map
```
### RViz
View just the `diffbot_description` in RViz.
```console
roslaunch diffbot_description view_diffbot.launch
```
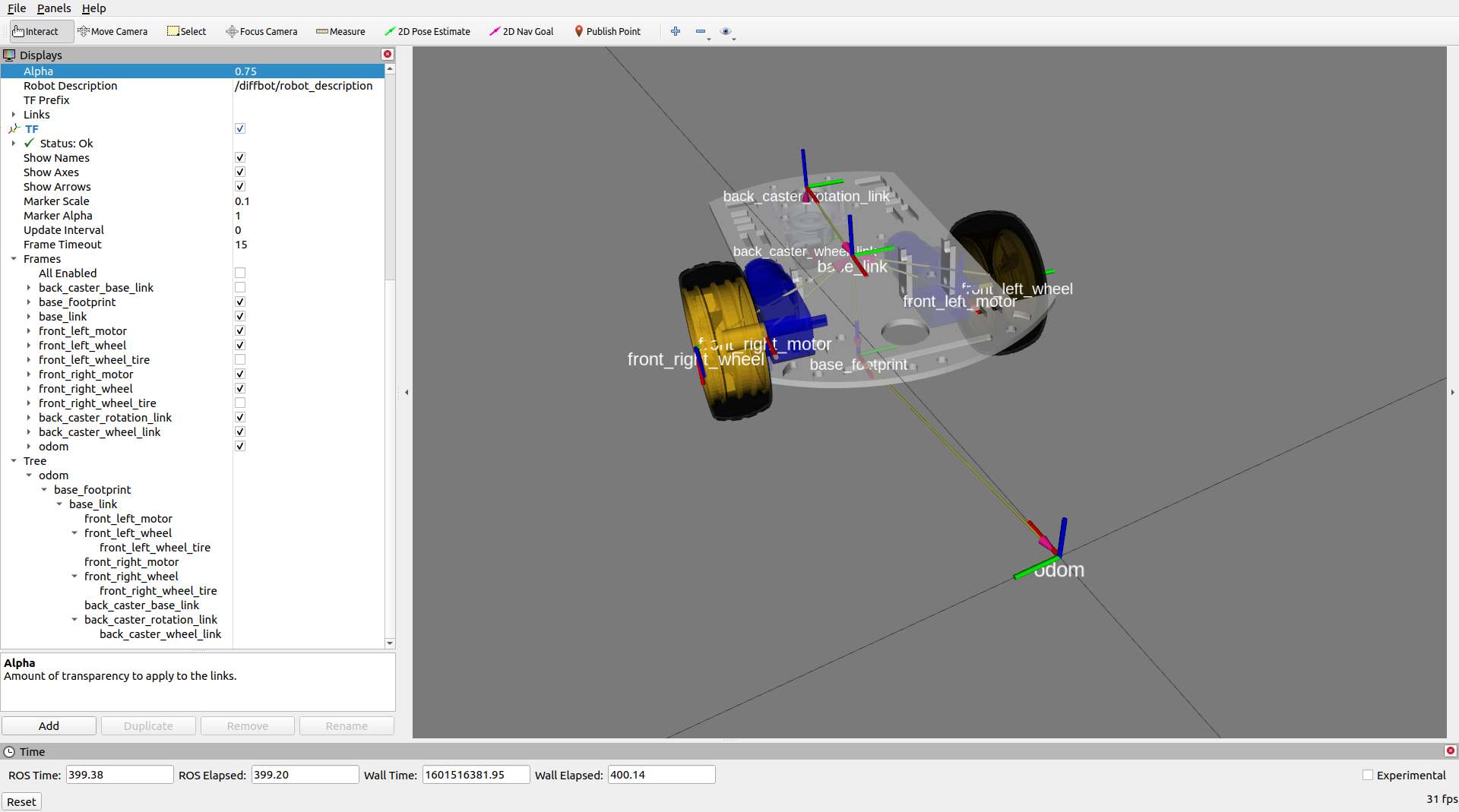
### Navigating and Mapping on the real Robot
The following video shows how to map a new environment and navigate in it
[
](https://youtu.be/2SwFTrJ1Ofg) |
## :package: 软件包概述
- [`diffbot_base`](./diffbot_base): 包含[`controller_manager`](http://wiki.ros.org/controller_manager)控制循环的ROS Control硬件接口,用于实际机器人。该包的[`scripts`文件夹](./diffbot_base/scripts)包含运行在Teensy微控制器上的低级`base_controller`。
- [`diffbot_bringup`](./diffbot_bringup): 用于启动实际DiffBot机器人的硬件驱动程序(相机、激光雷达、IMU、超声波等)的启动文件。
- [`diffbot_control`](./diffbot_control): Gazebo仿真和实际机器人中使用的ROS Control [`diff_drive_controller`](http://wiki.ros.org/diff_drive_controller)的配置。
- [`diffbot_description`](./diffbot_description): DiffBot及其传感器的URDF描述。
- [`diffbot_gazebo`](./diffbot_gazebo): DiffBot的仿真专用启动和配置文件。
- [`diffbot_msgs`](./diffbot_msgs): DiffBot特定的消息定义,例如编码器数据的消息。
- [`diffbot_navigation`](./diffbot_navigation): 基于[`move_base`包](http://wiki.ros.org/move_base)的导航;启动和配置文件。
- [`diffbot_slam`](./diffbot_slam): 使用不同实现(例如[gmapping](http://wiki.ros.org/gmapping))的同时定位与地图构建,用于创建环境地图。
## 安装
这些软件包是为[ROS 1 Noetic](http://wiki.ros.org/noetic)在[Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa](https://releases.ubuntu.com/20.04/)上编写和测试的。
对于实际机器人,[Ubuntu Mate 20.04](https://ubuntu-mate.org/download/arm64/focal/) arm64版本安装在4GB的[树莓派4 B](https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-4-model-b/)上。移动机器人和工作PC之间的通信通过配置[ROS网络](http://wiki.ros.org/ROS/NetworkSetup)完成,详见[文档](./docs/ros-network-setup.md)。
### 依赖项
所需的Ubuntu软件包列在[文档](https://ros-mobile-robots.com/packages/packages-setup/#obtain-system-dependencies)的软件包部分。其他ROS catkin软件包如[`rplidar_ros`](https://github.com/Slamtec/rplidar_ros)需要克隆到catkin工作空间中。
为了实现自动化和简化的依赖项安装过程,请安装[`vcstool`](https://github.com/dirk-thomas/vcstool),它将在后续步骤中使用。
```console
sudo apt install python3-vcstool
```
### :hammer: 如何构建
要构建此仓库中的软件包(包括Remo机器人),请按照以下步骤操作:
1. `cd`进入现有的ROS Noetic [catkin工作空间](http://wiki.ros.org/catkin/Tutorials/create_a_workspace)或创建一个新的:
```console
mkdir -p catkin_ws/src
```
2. 在ROS Noetic catkin工作空间的`src`文件夹中克隆此仓库:
```console
cd catkin_ws/src
```
```console
git clone https://github.com/fjp/diffbot.git
```
3. 从catkin工作空间的根目录执行`vcs import`命令,并根据执行命令的位置(开发PC或Remo的SBC)导入`diffbot_dev.repos`或`remo_robot.repos` YAML文件,以克隆列出的依赖项。仅在开发机器上运行以下命令:
```
vcs import < src/diffbot/diffbot_dev.repos
```
在Remo机器人的SBC上运行以下命令:
```
vcs import < src/diffbot/remo_robot.repos
```
4. 使用以下[`rosdep`命令](http://wiki.ros.org/rosdep#Install_dependency_of_all_packages_in_the_workspace)安装catkin工作空间中所有软件包所需的二进制依赖项:
```
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
```
5. 安装所需依赖项后,构建catkin工作空间,可以使用[`catkin_make`](http://wiki.ros.org/catkin/commands/catkin_make):
```console
catkin_ws$ catkin_make
```
或使用[catkin-tools](https://catkin-tools.readthedocs.io/en/latest/):
```console
catkin_ws$ catkin build
```
6. 最后,根据使用的shell,使用`devel/setup.*`脚本source新构建的软件包:
对于bash使用:
```console
catkin_ws$ source devel/setup.bash
```
对于zsh使用:
```console
catkin_ws$ source devel/setup.zsh
```
## 使用方法
以下部分描述如何运行机器人仿真以及如何使用可用的软件包启动文件使用实际硬件。
### 使用ROS Control的Gazebo仿真
Control the robot inside Gazebo and view what it sees in RViz using the following launch file:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_control diffbot.launch
```
这将启动默认的diffbot世界`db_world.world`。
要运行[turtlebot3_world](https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/turtlebot3_simulations/tree/master/turtlebot3_gazebo/models/turtlebot3_world),
请确保将其下载到`~/.gazebo/models/`文件夹中,因为`turtlebot3_world.world`文件引用了`turtlebot3_world`模型。
下载完成后,您可以使用以下命令运行它:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_control diffbot.launch world_name:='$(find diffbot_gazebo)/worlds/turtlebot3_world.world'
```
| `db_world.world` | `turtlebot3_world.world` |
|:-------------------------------------:|:--------------------------------:|
|  |  |
#### Navigation
要在Gazebo模拟器中的`db_world.world`环境中导航机器人,运行以下命令:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_navigation diffbot.launch
```
这使用了之前映射的`db_world.world`地图(位于[`diffbot_navigation/maps`](./diffbot_navigation/maps/)),该地图由[`map_server`](http://wiki.ros.org/map_server)提供服务。有了这个,你可以直接使用[RViz中的2D导航目标](http://wiki.ros.org/navigation/Tutorials/Using%20rviz%20with%20the%20Navigation%20Stack#A2D_Nav_Goal)让机器人在`db_world.world`中自主行驶。
[](https://youtu.be/2SwFTrJ1Ofg)
要运行`turtlebot3_world.world`(或您自己存储的世界和地图),请使用相同的`diffbot_navigation/launch/diffbot.launch`文件,但将`world_name`和`map_file`参数更改为您想要的世界和地图yaml文件:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_navigation diffbot.launch world_name:='$(find diffbot_gazebo)/worlds/turtlebot3_world.world' map_file:='$(find diffbot_navigation)/maps/map.yaml'
```
[](https://youtu.be/2SwFTrJ1Ofg)
#### SLAM
To map a new simulated environment using slam gmapping, first run
```console
roslaunch diffbot_gazebo diffbot.launch world_name:='$(find diffbot_gazebo)/worlds/turtlebot3_world.world'
```
and in a second terminal execute
```console
roslaunch diffbot_slam diffbot_slam.launch slam_method:=gmapping
```
Then explore the world with the [`teleop_twist_keyboard`](http://wiki.ros.org/teleop_twist_keyboard) or with the already launched [`rqt_robot_steering`](https://wiki.ros.org/rqt_robot_steering) GUI plugin:
[](https://youtu.be/gLlo5V-BZu0)
When you finished exploring the new world, use the [`map_saver`](http://wiki.ros.org/map_server#map_saver) node from the [`map_server`](http://wiki.ros.org/map_server) package to store the mapped enviornment:
```console
rosrun map_server map_saver -f ~/map
```
### RViz
View just the `diffbot_description` in RViz.
```console
roslaunch diffbot_description view_diffbot.launch
```

### Navigating and Mapping on the real Robot
The following video shows how to map a new environment and navigate in it
[ ](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik)
Start by setting up the ROS Network, by making the development PC the rosmaster (set the `ROS_MASTER_URI` environment variable accordingly, see [ROS Network Setup](https://ros-mobile-robots.com/ros-network-setup/) for more details),
Then follow the steps listed below to run the real Diffbot or Remo robot hardware:
1. First, brinup the robot hardware including its laser with the following launch file from the [`diffbot_bringup`](./diffbot_bringup) package.
Make sure to run this on the real robot (e.g. connect to it via `ssh`):
```console
roslaunch diffbot_bringup bringup_with_laser.launch
```
2. Then, in a new terminal on your remote/work development machine (not the single board computer) run the slam gmapping with the same command as in the simulation:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_slam diffbot_slam.launch slam_method:=gmapping
```
As you can see in the video, this should open up RViz and the [`rqt_robot_steering`](http://wiki.ros.org/rqt_robot_steering) plugin.
3. Next, steer the robot around manually either using the `keyboard_teleop` node or using the `rqt_robot_steering` node
and save the map with the following command when you are done exploring:
```console
rosrun map_server map_saver -f office
```
After the mapping process it is possible to use the created map for navigation, after running the following launch files:
1. On the single board computer (e.g. Raspberry Pi) make sure that the following is launched:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_bringup bringup_with_laser.launch
```
2. Then on the work/remote development machine run the `diffbot_hw.lauch` from the `diffbot_navigation` package:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_navigation diffbot_hw.lauch
```
Among other essential navigation and map server nodes, this will also launch an instance of RViz on your work pc where you can use its tools to:
1. Localize the robot with the "2D Pose Estimate" tool (green arrow) in RViz
2. Use the "2D Nav Goal" tool in RViz (red arrow) to send goals to the robot
## :construction: Future Work
Contributions to these tasks are welcome, see also the [contribution section](./README.md#contributions) below.
### ROS 2
- Migrate from ROS 1 to ROS 2
### Drivers, Odometry and Hardware Interface
- Add `diffbot_driver` package for ultrasonic ranger, imu and motor driver node code.
- Make use of the imu odometry data to improve the encoder odometry using a Kalman filter, such as [`robot_localization`](https://github.com/cra-ros-pkg/robot_localization) (or the less active [`robot_pose_ekf`](http://wiki.ros.org/robot_pose_ekf)).
- The current implementation of the ROS Control `hardware_interface::RobotHW` uses a high level PID controller. This is working but also
test a low level PID on the Teensy 3.2 mcu using the [Arduino library of the Grove i2c motor driver](https://github.com/Seeed-Studio/Grove_I2C_Motor_Driver_v1_3). -> This is partly implemented (see `diffbot_base/scripts/base_controller`)
Also replace `Wire.h` with the improved [`i2c_t3`](https://github.com/nox771/i2c_t3) library.
### Navigation
- Test different global and local planners and add documentation
- Add `diffbot_mbf` package using [`move_base_flex`](http://wiki.ros.org/move_base_flex), the improved version of [`move_base`](http://wiki.ros.org/move_base).
### Perception
To enable object detection or semantic segmentation with the RPi Camera the Raspberry Pi 4 B will be upated with a Google Coral USB Accelerator.
Possible useful packages:
- [MSeg](https://github.com/mseg-dataset/mseg-semantic)

### Teleoperation
- Use the generic [`teleop_twist_keyboard`](http://wiki.ros.org/teleop_twist_keyboard) and/or [`teleop_twist_joy`](http://wiki.ros.org/teleop_twist_joy) package to drive the real robot and in simulation.
- Playstation controller
### Tooling
- Use [clang format](https://clang.llvm.org/docs/ClangFormat.html) together with [`.clang-format`](https://github.com/PickNikRobotics/roscpp_code_format) file for `roscpp` to comply with [ROS C++ Style Guidelines](http://wiki.ros.org/CppStyleGuide)
## Part List Diffbot
| SBC RPi 4B | MCU Teensy 3.2 | IMU Bosch |
|:-------:|:-----------------:|:----:|
| [
](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik)
Start by setting up the ROS Network, by making the development PC the rosmaster (set the `ROS_MASTER_URI` environment variable accordingly, see [ROS Network Setup](https://ros-mobile-robots.com/ros-network-setup/) for more details),
Then follow the steps listed below to run the real Diffbot or Remo robot hardware:
1. First, brinup the robot hardware including its laser with the following launch file from the [`diffbot_bringup`](./diffbot_bringup) package.
Make sure to run this on the real robot (e.g. connect to it via `ssh`):
```console
roslaunch diffbot_bringup bringup_with_laser.launch
```
2. Then, in a new terminal on your remote/work development machine (not the single board computer) run the slam gmapping with the same command as in the simulation:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_slam diffbot_slam.launch slam_method:=gmapping
```
As you can see in the video, this should open up RViz and the [`rqt_robot_steering`](http://wiki.ros.org/rqt_robot_steering) plugin.
3. Next, steer the robot around manually either using the `keyboard_teleop` node or using the `rqt_robot_steering` node
and save the map with the following command when you are done exploring:
```console
rosrun map_server map_saver -f office
```
After the mapping process it is possible to use the created map for navigation, after running the following launch files:
1. On the single board computer (e.g. Raspberry Pi) make sure that the following is launched:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_bringup bringup_with_laser.launch
```
2. Then on the work/remote development machine run the `diffbot_hw.lauch` from the `diffbot_navigation` package:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_navigation diffbot_hw.lauch
```
Among other essential navigation and map server nodes, this will also launch an instance of RViz on your work pc where you can use its tools to:
1. Localize the robot with the "2D Pose Estimate" tool (green arrow) in RViz
2. Use the "2D Nav Goal" tool in RViz (red arrow) to send goals to the robot
## :construction: Future Work
Contributions to these tasks are welcome, see also the [contribution section](./README.md#contributions) below.
### ROS 2
- Migrate from ROS 1 to ROS 2
### Drivers, Odometry and Hardware Interface
- Add `diffbot_driver` package for ultrasonic ranger, imu and motor driver node code.
- Make use of the imu odometry data to improve the encoder odometry using a Kalman filter, such as [`robot_localization`](https://github.com/cra-ros-pkg/robot_localization) (or the less active [`robot_pose_ekf`](http://wiki.ros.org/robot_pose_ekf)).
- The current implementation of the ROS Control `hardware_interface::RobotHW` uses a high level PID controller. This is working but also
test a low level PID on the Teensy 3.2 mcu using the [Arduino library of the Grove i2c motor driver](https://github.com/Seeed-Studio/Grove_I2C_Motor_Driver_v1_3). -> This is partly implemented (see `diffbot_base/scripts/base_controller`)
Also replace `Wire.h` with the improved [`i2c_t3`](https://github.com/nox771/i2c_t3) library.
### Navigation
- Test different global and local planners and add documentation
- Add `diffbot_mbf` package using [`move_base_flex`](http://wiki.ros.org/move_base_flex), the improved version of [`move_base`](http://wiki.ros.org/move_base).
### Perception
To enable object detection or semantic segmentation with the RPi Camera the Raspberry Pi 4 B will be upated with a Google Coral USB Accelerator.
Possible useful packages:
- [MSeg](https://github.com/mseg-dataset/mseg-semantic)

### Teleoperation
- Use the generic [`teleop_twist_keyboard`](http://wiki.ros.org/teleop_twist_keyboard) and/or [`teleop_twist_joy`](http://wiki.ros.org/teleop_twist_joy) package to drive the real robot and in simulation.
- Playstation controller
### Tooling
- Use [clang format](https://clang.llvm.org/docs/ClangFormat.html) together with [`.clang-format`](https://github.com/PickNikRobotics/roscpp_code_format) file for `roscpp` to comply with [ROS C++ Style Guidelines](http://wiki.ros.org/CppStyleGuide)
## Part List Diffbot
| SBC RPi 4B | MCU Teensy 3.2 | IMU Bosch |
|:-------:|:-----------------:|:----:|
| [ ](https://ros-mobile-robots.com/) | [
](https://ros-mobile-robots.com/) | [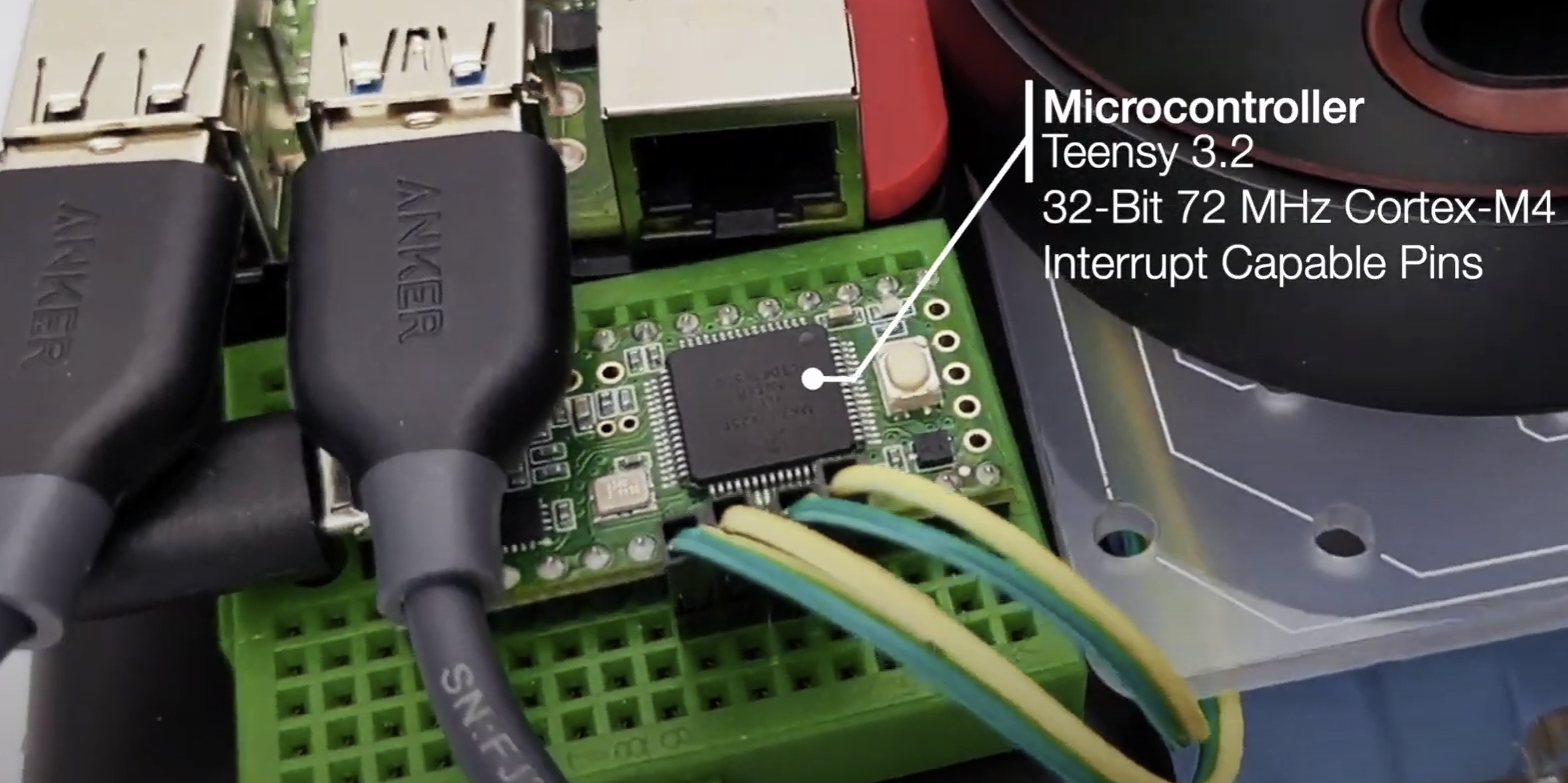 ](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/diffbot) | [
](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/diffbot) | [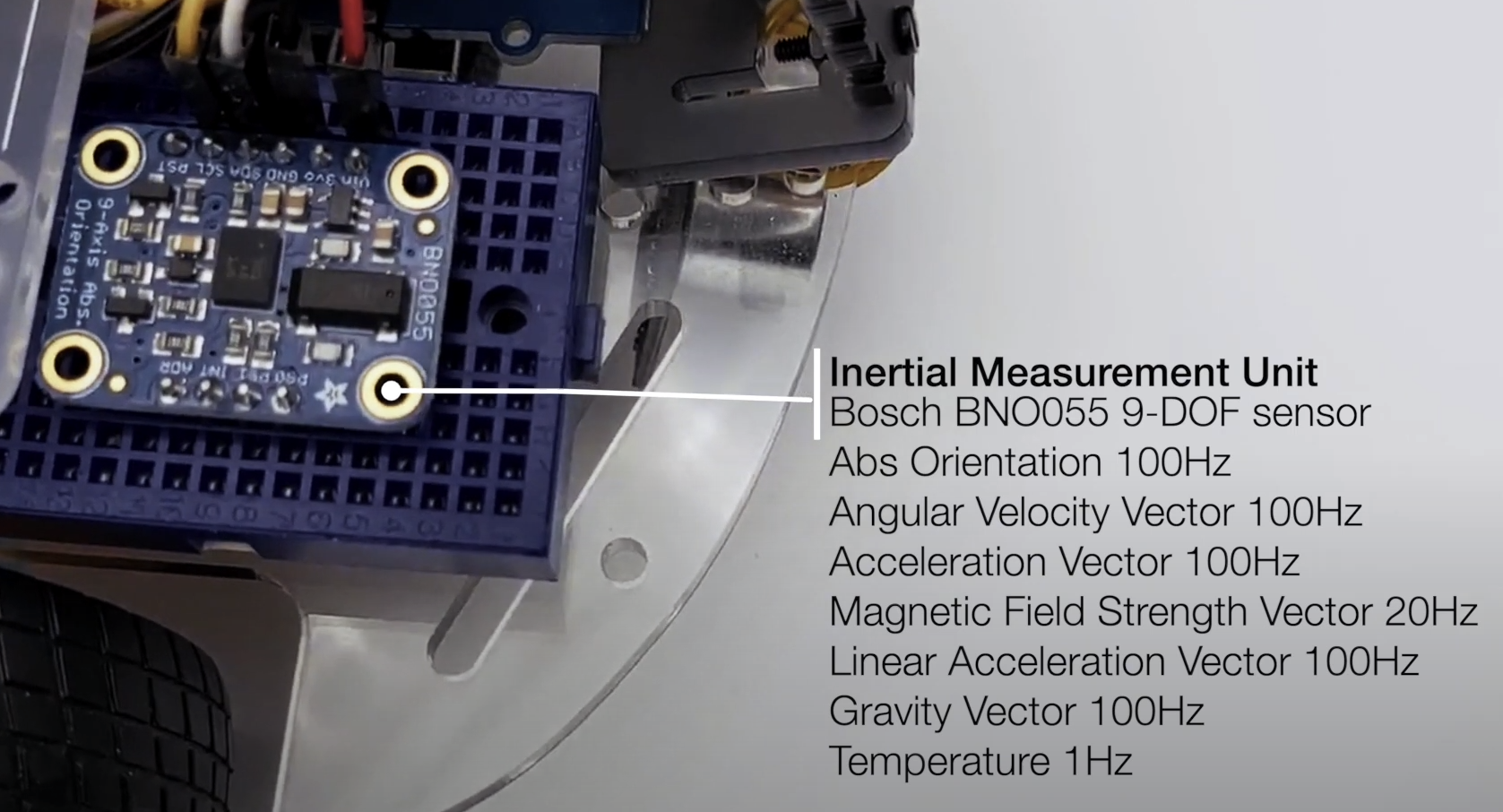 ](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/diffbot) |
| Part | Store |
|:------------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------:|
| Raspberry Pi 4 B (4 Gb) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3ltuJUo), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2IchIAc) |
| SanDisk 64 GB SD Card Class 10 | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2GLOyr0), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3dcFmYE) |
|Robot Smart Chassis Kit | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/34GXNAK), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2Gy3CJ4) |
| SLAMTEC RPLidar A2M8 (12 m) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3lthTFz), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/30MyImR) |
| Grove Ultrasonic Ranger | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/36M9TLS), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/34GZmyC) |
| Raspi Camera Module V2, 8 MP, 1080p | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2Ib9fgG), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2FdVDQF) |
| Grove Motor Driver | [seeedstudio.com](https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-I2C-Motor-Driver-with-L298.html), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/36M8O6M) |
| I2C Hub | [seeedstudio.com](https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-I2C-Hub.html), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/34CGEbz) |
| Teensy 4.0 or 3.2 | [PJRC Teensy 4.0](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy40.html), [PJRC Teensy 3.2](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy32.html) |
| Hobby Motor with Encoder - Metal Gear (DG01D-E) | [Sparkfun](https://www.sparkfun.com/products/16413) |
## Part List Remo
| Part | Store |
|:------------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------:|
| Raspberry Pi 4 B (4 Gb) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3ltuJUo), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2IchIAc) |
| SanDisk 64 GB SD Card Class 10 | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2GLOyr0), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3dcFmYE) |
| Remo Base | 3D printable, see [`remo_description`](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/remo_description) |
| SLAMTEC RPLidar A2M8 (12 m) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3lthTFz), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/30MyImR) |
| Raspi Camera Module V2, 8 MP, 1080p | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2Ib9fgG), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2FdVDQF) |
| Adafruit DC Motor (+ Stepper) FeatherWing | [adafruit.com](https://www.adafruit.com/product/2927), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3km5KF3) |
| Teensy 4.0 or 3.2 | [PJRC Teensy 4.0](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy40.html), [PJRC Teensy 3.2](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy32.html) |
| Hobby Motor with Encoder - Metal Gear (DG01D-E) | [Sparkfun](https://www.sparkfun.com/products/16413) |
| Powerbank (e.g 15000 mAh) | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3kmkx2t) This Powerbank from Goobay is close to the maximum possible size LxWxH: 135.5x70x18 mm) |
| Battery pack (for four or eight batteries) | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3kiX8PH) |
## Additional (Optional) Equipment
| Part | Store |
|:---------------------------------------|:------------------------------------:|
| PicoScope 3000 Series Oscilloscope 2CH | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/33I5tUb) |
| VOLTCRAFT PPS-16005 | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3iKsI4a) |
| 3D Printer for Remo's parts | [Prusa](https://shop.prusa3d.com/en/17-3d-printers), [Ultimaker](https://ultimaker.com/), etc. or use a local print service or an online one such as [Sculpteo](https://www.sculpteo.com/) |
## Hardware Architecture and Wiring
](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/diffbot) |
| Part | Store |
|:------------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------:|
| Raspberry Pi 4 B (4 Gb) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3ltuJUo), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2IchIAc) |
| SanDisk 64 GB SD Card Class 10 | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2GLOyr0), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3dcFmYE) |
|Robot Smart Chassis Kit | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/34GXNAK), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2Gy3CJ4) |
| SLAMTEC RPLidar A2M8 (12 m) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3lthTFz), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/30MyImR) |
| Grove Ultrasonic Ranger | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/36M9TLS), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/34GZmyC) |
| Raspi Camera Module V2, 8 MP, 1080p | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2Ib9fgG), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2FdVDQF) |
| Grove Motor Driver | [seeedstudio.com](https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-I2C-Motor-Driver-with-L298.html), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/36M8O6M) |
| I2C Hub | [seeedstudio.com](https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-I2C-Hub.html), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/34CGEbz) |
| Teensy 4.0 or 3.2 | [PJRC Teensy 4.0](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy40.html), [PJRC Teensy 3.2](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy32.html) |
| Hobby Motor with Encoder - Metal Gear (DG01D-E) | [Sparkfun](https://www.sparkfun.com/products/16413) |
## Part List Remo
| Part | Store |
|:------------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------:|
| Raspberry Pi 4 B (4 Gb) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3ltuJUo), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2IchIAc) |
| SanDisk 64 GB SD Card Class 10 | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2GLOyr0), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3dcFmYE) |
| Remo Base | 3D printable, see [`remo_description`](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/remo_description) |
| SLAMTEC RPLidar A2M8 (12 m) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3lthTFz), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/30MyImR) |
| Raspi Camera Module V2, 8 MP, 1080p | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2Ib9fgG), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2FdVDQF) |
| Adafruit DC Motor (+ Stepper) FeatherWing | [adafruit.com](https://www.adafruit.com/product/2927), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3km5KF3) |
| Teensy 4.0 or 3.2 | [PJRC Teensy 4.0](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy40.html), [PJRC Teensy 3.2](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy32.html) |
| Hobby Motor with Encoder - Metal Gear (DG01D-E) | [Sparkfun](https://www.sparkfun.com/products/16413) |
| Powerbank (e.g 15000 mAh) | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3kmkx2t) This Powerbank from Goobay is close to the maximum possible size LxWxH: 135.5x70x18 mm) |
| Battery pack (for four or eight batteries) | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3kiX8PH) |
## Additional (Optional) Equipment
| Part | Store |
|:---------------------------------------|:------------------------------------:|
| PicoScope 3000 Series Oscilloscope 2CH | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/33I5tUb) |
| VOLTCRAFT PPS-16005 | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3iKsI4a) |
| 3D Printer for Remo's parts | [Prusa](https://shop.prusa3d.com/en/17-3d-printers), [Ultimaker](https://ultimaker.com/), etc. or use a local print service or an online one such as [Sculpteo](https://www.sculpteo.com/) |
## Hardware Architecture and Wiring
DiffBot

Remo

## :handshake: Acknowledgment
- [Louis Morandy-Rapiné](https://louisrapine.com/) for his great work on [REMO robot](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/remo_description) and designing it in [Fusion 360](https://www.autodesk.com/products/fusion-360/overview).
- [Lentin Joseph](https://lentinjoseph.com/) and the participants of [ROS Developer Learning Path](https://robocademy.com/2020/06/25/enroll-in-robot-operating-system-learning-path-by-lentin-joseph/)
- The configurable `diffbot_description` using yaml files (see [ROS Wiki on xacro](http://wiki.ros.org/xacro#YAML_support)) is part of [`mobile_robot_description`](https://github.com/pxalcantara/mobile_robot_description) from [@pxalcantara](https://github.com/pxalcantara).
- Thanks to [@NestorDP](https://github.com/NestorDP) for help with the meshes (similar to [`littlebot`](https://github.com/NestorDP/littlebot)), see also [issue #1](https://github.com/fjp/diffbot/issues/1)
- [`dfki-ric/mir_robot`](https://github.com/dfki-ric/mir_robot)
- [`eborghi10/my_ROS_mobile_robot`](https://github.com/eborghi10/my_ROS_mobile_robot)
- [`husky`](https://github.com/husky/husky)
- [turtlebot3](https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/turtlebot3)
- [Linorobot](https://github.com/linorobot/linorobot)
## :wrench: Contributing
Your contributions are most welcome. These can be in the form of raising issues, creating PRs to correct or add documentation and of course solving existing issues or adding new features.
## :pencil: License
`diffbot` is licenses under the [BSD 3-Clause](./LICENSE).
See also [open-source-license-acknowledgements-and-third-party-copyrights.md](open-source-license-acknowledgements-and-third-party-copyrights.md).
The [documentation](https://ros-mobile-robots.com/) is licensed differently,
visit its [license text](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/ros-mobile-robots.github.io#license) to learn more. ](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik) | [
](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik) | [ ](https://fjp.at/projects/diffbot/) |
如果您正在寻找可3D打印的模块化底盘,请参见[`remo_description`](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/remo_description)仓库。您可以直接将其与此`diffbot`仓库的软件一起使用。
| Remo | Gazebo仿真 | RViz |
|:-------:|:-----------------:|:----:|
| [
](https://fjp.at/projects/diffbot/) |
如果您正在寻找可3D打印的模块化底盘,请参见[`remo_description`](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/remo_description)仓库。您可以直接将其与此`diffbot`仓库的软件一起使用。
| Remo | Gazebo仿真 | RViz |
|:-------:|:-----------------:|:----:|
| [ ](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik) | [
](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik) | [ ](https://github.com/fjp/diffbot) | [
](https://github.com/fjp/diffbot) | [ ](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/diffbot) |
它为不同的相机模块提供安装支架,如Raspi Cam v2、OAK-1、OAK-D,您甚至可以根据需要设计自己的支架。通过两个可更换的层板,它还支持不同的单板计算机(树莓派和Nvidia Jetson Nano)。您同样可以自由创建自己的层板。
## 演示
### SLAM和导航
| 实际机器人 | Gazebo仿真 |
|:-------:|:-----------------:|
| [
](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/diffbot) |
它为不同的相机模块提供安装支架,如Raspi Cam v2、OAK-1、OAK-D,您甚至可以根据需要设计自己的支架。通过两个可更换的层板,它还支持不同的单板计算机(树莓派和Nvidia Jetson Nano)。您同样可以自由创建自己的层板。
## 演示
### SLAM和导航
| 实际机器人 | Gazebo仿真 |
|:-------:|:-----------------:|
| [ ](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik) | [
](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik) | [ ](https://youtu.be/gLlo5V-BZu0) [
](https://youtu.be/gLlo5V-BZu0) [ ](https://youtu.be/2SwFTrJ1Ofg) |
## :package: 软件包概述
- [`diffbot_base`](./diffbot_base): 包含[`controller_manager`](http://wiki.ros.org/controller_manager)控制循环的ROS Control硬件接口,用于实际机器人。该包的[`scripts`文件夹](./diffbot_base/scripts)包含运行在Teensy微控制器上的低级`base_controller`。
- [`diffbot_bringup`](./diffbot_bringup): 用于启动实际DiffBot机器人的硬件驱动程序(相机、激光雷达、IMU、超声波等)的启动文件。
- [`diffbot_control`](./diffbot_control): Gazebo仿真和实际机器人中使用的ROS Control [`diff_drive_controller`](http://wiki.ros.org/diff_drive_controller)的配置。
- [`diffbot_description`](./diffbot_description): DiffBot及其传感器的URDF描述。
- [`diffbot_gazebo`](./diffbot_gazebo): DiffBot的仿真专用启动和配置文件。
- [`diffbot_msgs`](./diffbot_msgs): DiffBot特定的消息定义,例如编码器数据的消息。
- [`diffbot_navigation`](./diffbot_navigation): 基于[`move_base`包](http://wiki.ros.org/move_base)的导航;启动和配置文件。
- [`diffbot_slam`](./diffbot_slam): 使用不同实现(例如[gmapping](http://wiki.ros.org/gmapping))的同时定位与地图构建,用于创建环境地图。
## 安装
这些软件包是为[ROS 1 Noetic](http://wiki.ros.org/noetic)在[Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa](https://releases.ubuntu.com/20.04/)上编写和测试的。
对于实际机器人,[Ubuntu Mate 20.04](https://ubuntu-mate.org/download/arm64/focal/) arm64版本安装在4GB的[树莓派4 B](https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-4-model-b/)上。移动机器人和工作PC之间的通信通过配置[ROS网络](http://wiki.ros.org/ROS/NetworkSetup)完成,详见[文档](./docs/ros-network-setup.md)。
### 依赖项
所需的Ubuntu软件包列在[文档](https://ros-mobile-robots.com/packages/packages-setup/#obtain-system-dependencies)的软件包部分。其他ROS catkin软件包如[`rplidar_ros`](https://github.com/Slamtec/rplidar_ros)需要克隆到catkin工作空间中。
为了实现自动化和简化的依赖项安装过程,请安装[`vcstool`](https://github.com/dirk-thomas/vcstool),它将在后续步骤中使用。
```console
sudo apt install python3-vcstool
```
### :hammer: 如何构建
要构建此仓库中的软件包(包括Remo机器人),请按照以下步骤操作:
1. `cd`进入现有的ROS Noetic [catkin工作空间](http://wiki.ros.org/catkin/Tutorials/create_a_workspace)或创建一个新的:
```console
mkdir -p catkin_ws/src
```
2. 在ROS Noetic catkin工作空间的`src`文件夹中克隆此仓库:
```console
cd catkin_ws/src
```
```console
git clone https://github.com/fjp/diffbot.git
```
3. 从catkin工作空间的根目录执行`vcs import`命令,并根据执行命令的位置(开发PC或Remo的SBC)导入`diffbot_dev.repos`或`remo_robot.repos` YAML文件,以克隆列出的依赖项。仅在开发机器上运行以下命令:
```
vcs import < src/diffbot/diffbot_dev.repos
```
在Remo机器人的SBC上运行以下命令:
```
vcs import < src/diffbot/remo_robot.repos
```
4. 使用以下[`rosdep`命令](http://wiki.ros.org/rosdep#Install_dependency_of_all_packages_in_the_workspace)安装catkin工作空间中所有软件包所需的二进制依赖项:
```
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
```
5. 安装所需依赖项后,构建catkin工作空间,可以使用[`catkin_make`](http://wiki.ros.org/catkin/commands/catkin_make):
```console
catkin_ws$ catkin_make
```
或使用[catkin-tools](https://catkin-tools.readthedocs.io/en/latest/):
```console
catkin_ws$ catkin build
```
6. 最后,根据使用的shell,使用`devel/setup.*`脚本source新构建的软件包:
对于bash使用:
```console
catkin_ws$ source devel/setup.bash
```
对于zsh使用:
```console
catkin_ws$ source devel/setup.zsh
```
## 使用方法
以下部分描述如何运行机器人仿真以及如何使用可用的软件包启动文件使用实际硬件。
### 使用ROS Control的Gazebo仿真
Control the robot inside Gazebo and view what it sees in RViz using the following launch file:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_control diffbot.launch
```
这将启动默认的diffbot世界`db_world.world`。
要运行[turtlebot3_world](https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/turtlebot3_simulations/tree/master/turtlebot3_gazebo/models/turtlebot3_world),
请确保将其下载到`~/.gazebo/models/`文件夹中,因为`turtlebot3_world.world`文件引用了`turtlebot3_world`模型。
下载完成后,您可以使用以下命令运行它:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_control diffbot.launch world_name:='$(find diffbot_gazebo)/worlds/turtlebot3_world.world'
```
| `db_world.world` | `turtlebot3_world.world` |
|:-------------------------------------:|:--------------------------------:|
|  |  |
#### Navigation
要在Gazebo模拟器中的`db_world.world`环境中导航机器人,运行以下命令:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_navigation diffbot.launch
```
这使用了之前映射的`db_world.world`地图(位于[`diffbot_navigation/maps`](./diffbot_navigation/maps/)),该地图由[`map_server`](http://wiki.ros.org/map_server)提供服务。有了这个,你可以直接使用[RViz中的2D导航目标](http://wiki.ros.org/navigation/Tutorials/Using%20rviz%20with%20the%20Navigation%20Stack#A2D_Nav_Goal)让机器人在`db_world.world`中自主行驶。
[](https://youtu.be/2SwFTrJ1Ofg)
要运行`turtlebot3_world.world`(或您自己存储的世界和地图),请使用相同的`diffbot_navigation/launch/diffbot.launch`文件,但将`world_name`和`map_file`参数更改为您想要的世界和地图yaml文件:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_navigation diffbot.launch world_name:='$(find diffbot_gazebo)/worlds/turtlebot3_world.world' map_file:='$(find diffbot_navigation)/maps/map.yaml'
```
[](https://youtu.be/2SwFTrJ1Ofg)
#### SLAM
To map a new simulated environment using slam gmapping, first run
```console
roslaunch diffbot_gazebo diffbot.launch world_name:='$(find diffbot_gazebo)/worlds/turtlebot3_world.world'
```
and in a second terminal execute
```console
roslaunch diffbot_slam diffbot_slam.launch slam_method:=gmapping
```
Then explore the world with the [`teleop_twist_keyboard`](http://wiki.ros.org/teleop_twist_keyboard) or with the already launched [`rqt_robot_steering`](https://wiki.ros.org/rqt_robot_steering) GUI plugin:
[](https://youtu.be/gLlo5V-BZu0)
When you finished exploring the new world, use the [`map_saver`](http://wiki.ros.org/map_server#map_saver) node from the [`map_server`](http://wiki.ros.org/map_server) package to store the mapped enviornment:
```console
rosrun map_server map_saver -f ~/map
```
### RViz
View just the `diffbot_description` in RViz.
```console
roslaunch diffbot_description view_diffbot.launch
```

### Navigating and Mapping on the real Robot
The following video shows how to map a new environment and navigate in it
[
](https://youtu.be/2SwFTrJ1Ofg) |
## :package: 软件包概述
- [`diffbot_base`](./diffbot_base): 包含[`controller_manager`](http://wiki.ros.org/controller_manager)控制循环的ROS Control硬件接口,用于实际机器人。该包的[`scripts`文件夹](./diffbot_base/scripts)包含运行在Teensy微控制器上的低级`base_controller`。
- [`diffbot_bringup`](./diffbot_bringup): 用于启动实际DiffBot机器人的硬件驱动程序(相机、激光雷达、IMU、超声波等)的启动文件。
- [`diffbot_control`](./diffbot_control): Gazebo仿真和实际机器人中使用的ROS Control [`diff_drive_controller`](http://wiki.ros.org/diff_drive_controller)的配置。
- [`diffbot_description`](./diffbot_description): DiffBot及其传感器的URDF描述。
- [`diffbot_gazebo`](./diffbot_gazebo): DiffBot的仿真专用启动和配置文件。
- [`diffbot_msgs`](./diffbot_msgs): DiffBot特定的消息定义,例如编码器数据的消息。
- [`diffbot_navigation`](./diffbot_navigation): 基于[`move_base`包](http://wiki.ros.org/move_base)的导航;启动和配置文件。
- [`diffbot_slam`](./diffbot_slam): 使用不同实现(例如[gmapping](http://wiki.ros.org/gmapping))的同时定位与地图构建,用于创建环境地图。
## 安装
这些软件包是为[ROS 1 Noetic](http://wiki.ros.org/noetic)在[Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa](https://releases.ubuntu.com/20.04/)上编写和测试的。
对于实际机器人,[Ubuntu Mate 20.04](https://ubuntu-mate.org/download/arm64/focal/) arm64版本安装在4GB的[树莓派4 B](https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-4-model-b/)上。移动机器人和工作PC之间的通信通过配置[ROS网络](http://wiki.ros.org/ROS/NetworkSetup)完成,详见[文档](./docs/ros-network-setup.md)。
### 依赖项
所需的Ubuntu软件包列在[文档](https://ros-mobile-robots.com/packages/packages-setup/#obtain-system-dependencies)的软件包部分。其他ROS catkin软件包如[`rplidar_ros`](https://github.com/Slamtec/rplidar_ros)需要克隆到catkin工作空间中。
为了实现自动化和简化的依赖项安装过程,请安装[`vcstool`](https://github.com/dirk-thomas/vcstool),它将在后续步骤中使用。
```console
sudo apt install python3-vcstool
```
### :hammer: 如何构建
要构建此仓库中的软件包(包括Remo机器人),请按照以下步骤操作:
1. `cd`进入现有的ROS Noetic [catkin工作空间](http://wiki.ros.org/catkin/Tutorials/create_a_workspace)或创建一个新的:
```console
mkdir -p catkin_ws/src
```
2. 在ROS Noetic catkin工作空间的`src`文件夹中克隆此仓库:
```console
cd catkin_ws/src
```
```console
git clone https://github.com/fjp/diffbot.git
```
3. 从catkin工作空间的根目录执行`vcs import`命令,并根据执行命令的位置(开发PC或Remo的SBC)导入`diffbot_dev.repos`或`remo_robot.repos` YAML文件,以克隆列出的依赖项。仅在开发机器上运行以下命令:
```
vcs import < src/diffbot/diffbot_dev.repos
```
在Remo机器人的SBC上运行以下命令:
```
vcs import < src/diffbot/remo_robot.repos
```
4. 使用以下[`rosdep`命令](http://wiki.ros.org/rosdep#Install_dependency_of_all_packages_in_the_workspace)安装catkin工作空间中所有软件包所需的二进制依赖项:
```
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
```
5. 安装所需依赖项后,构建catkin工作空间,可以使用[`catkin_make`](http://wiki.ros.org/catkin/commands/catkin_make):
```console
catkin_ws$ catkin_make
```
或使用[catkin-tools](https://catkin-tools.readthedocs.io/en/latest/):
```console
catkin_ws$ catkin build
```
6. 最后,根据使用的shell,使用`devel/setup.*`脚本source新构建的软件包:
对于bash使用:
```console
catkin_ws$ source devel/setup.bash
```
对于zsh使用:
```console
catkin_ws$ source devel/setup.zsh
```
## 使用方法
以下部分描述如何运行机器人仿真以及如何使用可用的软件包启动文件使用实际硬件。
### 使用ROS Control的Gazebo仿真
Control the robot inside Gazebo and view what it sees in RViz using the following launch file:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_control diffbot.launch
```
这将启动默认的diffbot世界`db_world.world`。
要运行[turtlebot3_world](https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/turtlebot3_simulations/tree/master/turtlebot3_gazebo/models/turtlebot3_world),
请确保将其下载到`~/.gazebo/models/`文件夹中,因为`turtlebot3_world.world`文件引用了`turtlebot3_world`模型。
下载完成后,您可以使用以下命令运行它:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_control diffbot.launch world_name:='$(find diffbot_gazebo)/worlds/turtlebot3_world.world'
```
| `db_world.world` | `turtlebot3_world.world` |
|:-------------------------------------:|:--------------------------------:|
|  |  |
#### Navigation
要在Gazebo模拟器中的`db_world.world`环境中导航机器人,运行以下命令:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_navigation diffbot.launch
```
这使用了之前映射的`db_world.world`地图(位于[`diffbot_navigation/maps`](./diffbot_navigation/maps/)),该地图由[`map_server`](http://wiki.ros.org/map_server)提供服务。有了这个,你可以直接使用[RViz中的2D导航目标](http://wiki.ros.org/navigation/Tutorials/Using%20rviz%20with%20the%20Navigation%20Stack#A2D_Nav_Goal)让机器人在`db_world.world`中自主行驶。
[](https://youtu.be/2SwFTrJ1Ofg)
要运行`turtlebot3_world.world`(或您自己存储的世界和地图),请使用相同的`diffbot_navigation/launch/diffbot.launch`文件,但将`world_name`和`map_file`参数更改为您想要的世界和地图yaml文件:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_navigation diffbot.launch world_name:='$(find diffbot_gazebo)/worlds/turtlebot3_world.world' map_file:='$(find diffbot_navigation)/maps/map.yaml'
```
[](https://youtu.be/2SwFTrJ1Ofg)
#### SLAM
To map a new simulated environment using slam gmapping, first run
```console
roslaunch diffbot_gazebo diffbot.launch world_name:='$(find diffbot_gazebo)/worlds/turtlebot3_world.world'
```
and in a second terminal execute
```console
roslaunch diffbot_slam diffbot_slam.launch slam_method:=gmapping
```
Then explore the world with the [`teleop_twist_keyboard`](http://wiki.ros.org/teleop_twist_keyboard) or with the already launched [`rqt_robot_steering`](https://wiki.ros.org/rqt_robot_steering) GUI plugin:
[](https://youtu.be/gLlo5V-BZu0)
When you finished exploring the new world, use the [`map_saver`](http://wiki.ros.org/map_server#map_saver) node from the [`map_server`](http://wiki.ros.org/map_server) package to store the mapped enviornment:
```console
rosrun map_server map_saver -f ~/map
```
### RViz
View just the `diffbot_description` in RViz.
```console
roslaunch diffbot_description view_diffbot.launch
```

### Navigating and Mapping on the real Robot
The following video shows how to map a new environment and navigate in it
[ ](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik)
Start by setting up the ROS Network, by making the development PC the rosmaster (set the `ROS_MASTER_URI` environment variable accordingly, see [ROS Network Setup](https://ros-mobile-robots.com/ros-network-setup/) for more details),
Then follow the steps listed below to run the real Diffbot or Remo robot hardware:
1. First, brinup the robot hardware including its laser with the following launch file from the [`diffbot_bringup`](./diffbot_bringup) package.
Make sure to run this on the real robot (e.g. connect to it via `ssh`):
```console
roslaunch diffbot_bringup bringup_with_laser.launch
```
2. Then, in a new terminal on your remote/work development machine (not the single board computer) run the slam gmapping with the same command as in the simulation:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_slam diffbot_slam.launch slam_method:=gmapping
```
As you can see in the video, this should open up RViz and the [`rqt_robot_steering`](http://wiki.ros.org/rqt_robot_steering) plugin.
3. Next, steer the robot around manually either using the `keyboard_teleop` node or using the `rqt_robot_steering` node
and save the map with the following command when you are done exploring:
```console
rosrun map_server map_saver -f office
```
After the mapping process it is possible to use the created map for navigation, after running the following launch files:
1. On the single board computer (e.g. Raspberry Pi) make sure that the following is launched:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_bringup bringup_with_laser.launch
```
2. Then on the work/remote development machine run the `diffbot_hw.lauch` from the `diffbot_navigation` package:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_navigation diffbot_hw.lauch
```
Among other essential navigation and map server nodes, this will also launch an instance of RViz on your work pc where you can use its tools to:
1. Localize the robot with the "2D Pose Estimate" tool (green arrow) in RViz
2. Use the "2D Nav Goal" tool in RViz (red arrow) to send goals to the robot
## :construction: Future Work
Contributions to these tasks are welcome, see also the [contribution section](./README.md#contributions) below.
### ROS 2
- Migrate from ROS 1 to ROS 2
### Drivers, Odometry and Hardware Interface
- Add `diffbot_driver` package for ultrasonic ranger, imu and motor driver node code.
- Make use of the imu odometry data to improve the encoder odometry using a Kalman filter, such as [`robot_localization`](https://github.com/cra-ros-pkg/robot_localization) (or the less active [`robot_pose_ekf`](http://wiki.ros.org/robot_pose_ekf)).
- The current implementation of the ROS Control `hardware_interface::RobotHW` uses a high level PID controller. This is working but also
test a low level PID on the Teensy 3.2 mcu using the [Arduino library of the Grove i2c motor driver](https://github.com/Seeed-Studio/Grove_I2C_Motor_Driver_v1_3). -> This is partly implemented (see `diffbot_base/scripts/base_controller`)
Also replace `Wire.h` with the improved [`i2c_t3`](https://github.com/nox771/i2c_t3) library.
### Navigation
- Test different global and local planners and add documentation
- Add `diffbot_mbf` package using [`move_base_flex`](http://wiki.ros.org/move_base_flex), the improved version of [`move_base`](http://wiki.ros.org/move_base).
### Perception
To enable object detection or semantic segmentation with the RPi Camera the Raspberry Pi 4 B will be upated with a Google Coral USB Accelerator.
Possible useful packages:
- [MSeg](https://github.com/mseg-dataset/mseg-semantic)

### Teleoperation
- Use the generic [`teleop_twist_keyboard`](http://wiki.ros.org/teleop_twist_keyboard) and/or [`teleop_twist_joy`](http://wiki.ros.org/teleop_twist_joy) package to drive the real robot and in simulation.
- Playstation controller
### Tooling
- Use [clang format](https://clang.llvm.org/docs/ClangFormat.html) together with [`.clang-format`](https://github.com/PickNikRobotics/roscpp_code_format) file for `roscpp` to comply with [ROS C++ Style Guidelines](http://wiki.ros.org/CppStyleGuide)
## Part List Diffbot
| SBC RPi 4B | MCU Teensy 3.2 | IMU Bosch |
|:-------:|:-----------------:|:----:|
| [
](https://youtu.be/IcYkQyzUqik)
Start by setting up the ROS Network, by making the development PC the rosmaster (set the `ROS_MASTER_URI` environment variable accordingly, see [ROS Network Setup](https://ros-mobile-robots.com/ros-network-setup/) for more details),
Then follow the steps listed below to run the real Diffbot or Remo robot hardware:
1. First, brinup the robot hardware including its laser with the following launch file from the [`diffbot_bringup`](./diffbot_bringup) package.
Make sure to run this on the real robot (e.g. connect to it via `ssh`):
```console
roslaunch diffbot_bringup bringup_with_laser.launch
```
2. Then, in a new terminal on your remote/work development machine (not the single board computer) run the slam gmapping with the same command as in the simulation:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_slam diffbot_slam.launch slam_method:=gmapping
```
As you can see in the video, this should open up RViz and the [`rqt_robot_steering`](http://wiki.ros.org/rqt_robot_steering) plugin.
3. Next, steer the robot around manually either using the `keyboard_teleop` node or using the `rqt_robot_steering` node
and save the map with the following command when you are done exploring:
```console
rosrun map_server map_saver -f office
```
After the mapping process it is possible to use the created map for navigation, after running the following launch files:
1. On the single board computer (e.g. Raspberry Pi) make sure that the following is launched:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_bringup bringup_with_laser.launch
```
2. Then on the work/remote development machine run the `diffbot_hw.lauch` from the `diffbot_navigation` package:
```console
roslaunch diffbot_navigation diffbot_hw.lauch
```
Among other essential navigation and map server nodes, this will also launch an instance of RViz on your work pc where you can use its tools to:
1. Localize the robot with the "2D Pose Estimate" tool (green arrow) in RViz
2. Use the "2D Nav Goal" tool in RViz (red arrow) to send goals to the robot
## :construction: Future Work
Contributions to these tasks are welcome, see also the [contribution section](./README.md#contributions) below.
### ROS 2
- Migrate from ROS 1 to ROS 2
### Drivers, Odometry and Hardware Interface
- Add `diffbot_driver` package for ultrasonic ranger, imu and motor driver node code.
- Make use of the imu odometry data to improve the encoder odometry using a Kalman filter, such as [`robot_localization`](https://github.com/cra-ros-pkg/robot_localization) (or the less active [`robot_pose_ekf`](http://wiki.ros.org/robot_pose_ekf)).
- The current implementation of the ROS Control `hardware_interface::RobotHW` uses a high level PID controller. This is working but also
test a low level PID on the Teensy 3.2 mcu using the [Arduino library of the Grove i2c motor driver](https://github.com/Seeed-Studio/Grove_I2C_Motor_Driver_v1_3). -> This is partly implemented (see `diffbot_base/scripts/base_controller`)
Also replace `Wire.h` with the improved [`i2c_t3`](https://github.com/nox771/i2c_t3) library.
### Navigation
- Test different global and local planners and add documentation
- Add `diffbot_mbf` package using [`move_base_flex`](http://wiki.ros.org/move_base_flex), the improved version of [`move_base`](http://wiki.ros.org/move_base).
### Perception
To enable object detection or semantic segmentation with the RPi Camera the Raspberry Pi 4 B will be upated with a Google Coral USB Accelerator.
Possible useful packages:
- [MSeg](https://github.com/mseg-dataset/mseg-semantic)

### Teleoperation
- Use the generic [`teleop_twist_keyboard`](http://wiki.ros.org/teleop_twist_keyboard) and/or [`teleop_twist_joy`](http://wiki.ros.org/teleop_twist_joy) package to drive the real robot and in simulation.
- Playstation controller
### Tooling
- Use [clang format](https://clang.llvm.org/docs/ClangFormat.html) together with [`.clang-format`](https://github.com/PickNikRobotics/roscpp_code_format) file for `roscpp` to comply with [ROS C++ Style Guidelines](http://wiki.ros.org/CppStyleGuide)
## Part List Diffbot
| SBC RPi 4B | MCU Teensy 3.2 | IMU Bosch |
|:-------:|:-----------------:|:----:|
| [ ](https://ros-mobile-robots.com/) | [
](https://ros-mobile-robots.com/) | [ ](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/diffbot) | [
](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/diffbot) | [ ](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/diffbot) |
| Part | Store |
|:------------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------:|
| Raspberry Pi 4 B (4 Gb) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3ltuJUo), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2IchIAc) |
| SanDisk 64 GB SD Card Class 10 | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2GLOyr0), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3dcFmYE) |
|Robot Smart Chassis Kit | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/34GXNAK), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2Gy3CJ4) |
| SLAMTEC RPLidar A2M8 (12 m) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3lthTFz), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/30MyImR) |
| Grove Ultrasonic Ranger | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/36M9TLS), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/34GZmyC) |
| Raspi Camera Module V2, 8 MP, 1080p | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2Ib9fgG), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2FdVDQF) |
| Grove Motor Driver | [seeedstudio.com](https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-I2C-Motor-Driver-with-L298.html), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/36M8O6M) |
| I2C Hub | [seeedstudio.com](https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-I2C-Hub.html), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/34CGEbz) |
| Teensy 4.0 or 3.2 | [PJRC Teensy 4.0](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy40.html), [PJRC Teensy 3.2](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy32.html) |
| Hobby Motor with Encoder - Metal Gear (DG01D-E) | [Sparkfun](https://www.sparkfun.com/products/16413) |
## Part List Remo
| Part | Store |
|:------------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------:|
| Raspberry Pi 4 B (4 Gb) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3ltuJUo), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2IchIAc) |
| SanDisk 64 GB SD Card Class 10 | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2GLOyr0), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3dcFmYE) |
| Remo Base | 3D printable, see [`remo_description`](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/remo_description) |
| SLAMTEC RPLidar A2M8 (12 m) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3lthTFz), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/30MyImR) |
| Raspi Camera Module V2, 8 MP, 1080p | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2Ib9fgG), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2FdVDQF) |
| Adafruit DC Motor (+ Stepper) FeatherWing | [adafruit.com](https://www.adafruit.com/product/2927), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3km5KF3) |
| Teensy 4.0 or 3.2 | [PJRC Teensy 4.0](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy40.html), [PJRC Teensy 3.2](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy32.html) |
| Hobby Motor with Encoder - Metal Gear (DG01D-E) | [Sparkfun](https://www.sparkfun.com/products/16413) |
| Powerbank (e.g 15000 mAh) | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3kmkx2t) This Powerbank from Goobay is close to the maximum possible size LxWxH: 135.5x70x18 mm) |
| Battery pack (for four or eight batteries) | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3kiX8PH) |
## Additional (Optional) Equipment
| Part | Store |
|:---------------------------------------|:------------------------------------:|
| PicoScope 3000 Series Oscilloscope 2CH | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/33I5tUb) |
| VOLTCRAFT PPS-16005 | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3iKsI4a) |
| 3D Printer for Remo's parts | [Prusa](https://shop.prusa3d.com/en/17-3d-printers), [Ultimaker](https://ultimaker.com/), etc. or use a local print service or an online one such as [Sculpteo](https://www.sculpteo.com/) |
## Hardware Architecture and Wiring
](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/diffbot) |
| Part | Store |
|:------------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------:|
| Raspberry Pi 4 B (4 Gb) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3ltuJUo), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2IchIAc) |
| SanDisk 64 GB SD Card Class 10 | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2GLOyr0), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3dcFmYE) |
|Robot Smart Chassis Kit | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/34GXNAK), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2Gy3CJ4) |
| SLAMTEC RPLidar A2M8 (12 m) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3lthTFz), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/30MyImR) |
| Grove Ultrasonic Ranger | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/36M9TLS), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/34GZmyC) |
| Raspi Camera Module V2, 8 MP, 1080p | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2Ib9fgG), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2FdVDQF) |
| Grove Motor Driver | [seeedstudio.com](https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-I2C-Motor-Driver-with-L298.html), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/36M8O6M) |
| I2C Hub | [seeedstudio.com](https://www.seeedstudio.com/Grove-I2C-Hub.html), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/34CGEbz) |
| Teensy 4.0 or 3.2 | [PJRC Teensy 4.0](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy40.html), [PJRC Teensy 3.2](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy32.html) |
| Hobby Motor with Encoder - Metal Gear (DG01D-E) | [Sparkfun](https://www.sparkfun.com/products/16413) |
## Part List Remo
| Part | Store |
|:------------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------:|
| Raspberry Pi 4 B (4 Gb) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3ltuJUo), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2IchIAc) |
| SanDisk 64 GB SD Card Class 10 | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2GLOyr0), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3dcFmYE) |
| Remo Base | 3D printable, see [`remo_description`](https://github.com/ros-mobile-robots/remo_description) |
| SLAMTEC RPLidar A2M8 (12 m) | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/3lthTFz), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/30MyImR) |
| Raspi Camera Module V2, 8 MP, 1080p | [Amazon.com](https://amzn.to/2Ib9fgG), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/2FdVDQF) |
| Adafruit DC Motor (+ Stepper) FeatherWing | [adafruit.com](https://www.adafruit.com/product/2927), [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3km5KF3) |
| Teensy 4.0 or 3.2 | [PJRC Teensy 4.0](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy40.html), [PJRC Teensy 3.2](https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy32.html) |
| Hobby Motor with Encoder - Metal Gear (DG01D-E) | [Sparkfun](https://www.sparkfun.com/products/16413) |
| Powerbank (e.g 15000 mAh) | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3kmkx2t) This Powerbank from Goobay is close to the maximum possible size LxWxH: 135.5x70x18 mm) |
| Battery pack (for four or eight batteries) | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3kiX8PH) |
## Additional (Optional) Equipment
| Part | Store |
|:---------------------------------------|:------------------------------------:|
| PicoScope 3000 Series Oscilloscope 2CH | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/33I5tUb) |
| VOLTCRAFT PPS-16005 | [Amazon.de](https://amzn.to/3iKsI4a) |
| 3D Printer for Remo's parts | [Prusa](https://shop.prusa3d.com/en/17-3d-printers), [Ultimaker](https://ultimaker.com/), etc. or use a local print service or an online one such as [Sculpteo](https://www.sculpteo.com/) |
## Hardware Architecture and Wiring